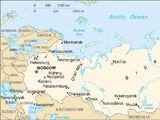
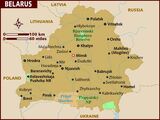
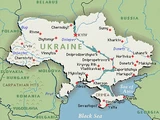
The Soviet Union was formally divided into a number of Union Republics encompassing various areas of the nation. The largest of these was the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, comprising about 60% of Soviet territory.
At different points in its history, there were nineteen other republics, which were named as Soviet Socialist Republics. Sixteen were established at the creation of the Soviet Union; of these, four were eventually dissolved among the territories of other republics.
Four others were created during the expansionism of 1940: The Karelo-Finnish SSR, which was created from territory conquered from Finland in the Winter War, lost and then regained during the Continuation War, and eventually subsumed into the Russian SFSR in 1956. Today this territory is the Republic of Karelia, an autonomous subdivision of the Russian Federation.
The other three republics added in 1940 were the Estonian, Latvian, and Lithuanian SSRs, whose legal status did not change from 1940 to 1992. When those countries achieved independence, their governments maintained that the USSR's annexation of their territories had been unlawful and that they had never been Soviet republics but sovereign nations subject to occupation, a position which is supported by the United States, the European Union, and the United Nations.
Constitutionally, the Soviet Union was a federation, but in practice its national government remained highly centralized from its inception until the glasnost and perestroika reforms of the 1980s. All three of the Soviet Union's constitutions (1922, 1936, and 1977) afforded each republic the right of secession. This legality was considered meaningless throughout most of Soviet history. The right to secession was invoked by the Russian SFSR and the Ukrainian and Belorussian SSRs on December 25, 1991; these three secessions led directly to the dissolution of the Soviet Union the next day. Russia was quickly recognized as the USSR's successor state.
Today each of the fifteen states which held republican status at the time of the USSR's dissolution is a sovereign nation. Upon the dissolution, a very loose federation known as the Commonwealth of Independent States was created by their respective governments. Most former Soviet republics belong to the CIS. Ukraine is a participating non-member, Turkmenistan is an associate member, and Georgia is a former member who withdrew in protest of the CIS's pro-Russian policy during Russia's 2008 invasion of Georgia. Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania have never participated in the CIS, for fear that membership would undercut their claim that their annexation to the USSR was never lawful.
All items (10)